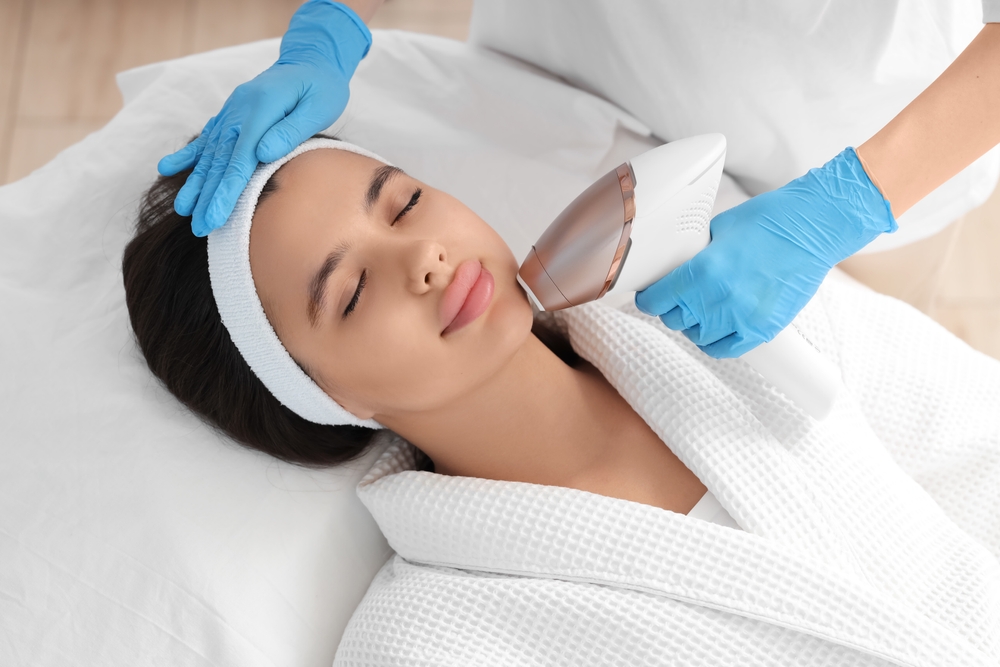

Everything You Need to Know About IPL Laser Treatment
In the evolving world of advanced skincare, IPL laser treatment has become one of the most sought-after solutions for those looking to improve skin clarity,
Our unique approach enables us to look beneath the surface of the skin and simulate your results prior to treatment. Learn more >
Results simulator now available. Learn more >

Understanding how much protein you can absorb at once is key to optimising your diet, whether you’re trying to build muscle, manage your weight, or simply maintain a healthy lifestyle. Many myths surround how much protein can you absorb at once, leading to confusion about the best way to consume this vital nutrient.
In this article, we’ll break down the science behind protein absorption and explore how much protein your body can handle in a single meal, as well as how to spread intake throughout the day for optimal benefits.
Your body requires protein to perform various functions, from muscle repair to supporting immune health. However, there’s often confusion around how much protein your body can actually absorb in one go.
To clarify, how much protein can you absorb at once depends on several factors including age, muscle mass, and activity level.
Research suggests that most people can absorb between 25-35 grams of protein per meal. For highly active individuals, this number may go slightly higher, but exceeding 40 grams at once might not offer significant benefits in terms of muscle growth or repair.
The digestive system processes protein before it can be absorbed. It is estimated that how much protein can you digest at once varies, but generally, the body effectively digests and absorbs up to 40 grams of protein in one meal.
Consuming more than this may lead to the surplus being stored as fat or utilised for energy, rather than contributing to muscle synthesis.
To get the most out of your meals, it’s better to focus on the quality of the protein rather than trying to force higher quantities in one go. For example, protein from lean meats, fish, and plant sources like legumes and tofu tend to be easier for the body to digest and absorb.
Several factors influence how much protein can your body intake at one time. These include:
As people age, their body’s ability to absorb and utilise protein efficiently tends to decline. This process, known as anabolic resistance, means that older adults may require more protein to achieve the same muscle-building and maintenance benefits as younger individuals.
Several factors contribute to reduced protein absorption in older adults.
These include a decrease in muscle mass, slower digestion, and less efficient synthesis of muscle proteins. Additionally, hormonal changes during menopause and the presence of chronic conditions can also affect how well protein is absorbed and utilised by the body.
To counteract this, it’s important for older adults to increase their protein intake, both in terms of quantity and quality. Consuming high-quality protein sources, such as lean meats, eggs, dairy, and plant-based options like legumes and tofu, can help maintain muscle mass, support immune function, and promote overall health.
Increased protein intake can also reduce the risk of sarcopenia, a condition characterised by the gradual loss of muscle mass and strength, which can significantly impact mobility and independence.
While you may be able to digest and absorb 30-40 grams of protein in a meal, the body’s ability to utilise this protein for muscle synthesis plateaus.
This means that for muscle building purposes, there’s little advantage to consuming large amounts of protein in one sitting. Instead, it’s better to spread out protein intake across multiple meals throughout the day.
For example:
Meal timing has been a topic of debate, particularly when it comes to protein absorption. Does when you eat protein influence how effectively your body uses it?
While the amount and quality of protein consumed are key factors, the timing of intake can also impact workout recovery and muscle synthesis.
For individuals engaging in physical activity, especially resistance or weight training, protein timing plays a role in muscle recovery.
Consuming protein during the anabolic window – typically within 30 to 60 minutes post-exercise – can improve muscle repair and growth due to the body’s heightened ability to use protein after training.
Key points include:
In relation to daily activities, timing is less critical, but distributing protein intake throughout the day is ideal for maximising muscle synthesis. Benefits of spreading protein across meals include:
Conversely, consuming large quantities of protein in one sitting, especially during sedentary periods, may not provide additional muscle-building benefits. Excess protein could be stored as fat or used for energy.
The key to effective protein absorption lies in spreading your intake across meals. Research indicates that consuming 25-35 grams per meal is a good target for most people. If you are highly active or looking to build muscle, aim towards the higher end of this range, but avoid trying to consume it all at once.
By spacing out your meals and snacks, you allow your body to efficiently absorb and utilise the protein. For example, consuming 30 grams of protein from lean meats or plant-based sources like chickpeas or tofu at lunch will support muscle synthesis and overall health.
When considering how much protein your body can intake during the day, it’s important to customise it based on individual goals. Whether you’re working towards muscle growth or skin health, protein plays a crucial role in recovery and maintenance.
For example, if you’re considering a facial Sydney cosmetic Clinic treatment, adequate protein intake can aid in the skin’s healing process, supporting better results.
Protein sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, and plant-based options such as beans and legumes provide a great way to meet your daily protein needs.
If weight loss is your goal, protein still plays a crucial role. High-protein meals can help you feel fuller for longer, reduce cravings, and prevent muscle loss during periods of calorie restriction. Additionally, adequate protein intake is key to maintaining healthy skin.
By supporting skin elasticity and tissue repair, protein helps you achieve not only your weight goals but also the best skin of your life, especially when combined with skin treatments.
Moreover, incorporating high-protein snacks such as Greek yoghurt, nuts, or protein shakes between meals helps manage hunger and supports a more balanced diet.
For individuals concerned about skin health, protein plays a role in supporting skin elasticity and repair. At the Sydney Cosmetic Clinic, health professionals often recommend balanced diets, which include adequate protein for skin health, particularly for those undergoing treatments.
For those recovering from medical treatments such as skin cancer therapies at Sydney Cosmetic Clinic, protein is essential in promoting wound healing and tissue regeneration. The inclusion of enough protein in the diet can expedite recovery, reduce inflammation, and support overall skin health.
For those frequenting the gym, athletes, or anyone who follows a rigorous training schedule, optimising protein intake becomes crucial. Active individuals, especially those engaging in weight training, need to ensure they meet their protein needs consistently throughout the day to support muscle repair and growth.
This is where strategies such as pre- and post-workout nutrition come into play. For instance, consuming 20-25 grams of protein within an hour after exercise can significantly aid muscle recovery.
After a rejuvenating session at a Sydney Cosmetic Clinic, your body requires proper nutrition to restore and refresh muscles. Ensuring that your post-spa meal includes a source of lean protein can help in muscle recovery and relaxation, extending the benefits of the spa treatment.
Protein is crucial for various bodily functions, and insufficient intake can lead to several negative consequences.
One of the main issues is muscle loss. Without adequate protein, your body may begin to break down muscle tissue to meet its protein needs, resulting in sarcopenia, the gradual decline in muscle mass. This can affect individuals of any age but is particularly concerning for older adults.
In terms of weight management, a lack of protein can lead to:
Other health concerns related to inadequate protein intake include:
Most people benefit from spreading protein intake throughout the day, aiming for 25-35 grams per meal. Factors such as activity level, body weight, and age all play a role in determining your specific needs.
Remember, balance is key – consuming excessive protein in one sitting may not provide additional benefits. Instead, focus on consistent and quality protein sources for optimal health.
If you’re looking to boost how much protein can you absorb at once and improve your health, consider complementary cosmetic treatments. At Sydney Cosmetic Clinic, we offer services designed to support post-weight-loss goals and help you feel your best. Visit us today!

In the evolving world of advanced skincare, IPL laser treatment has become one of the most sought-after solutions for those looking to improve skin clarity,
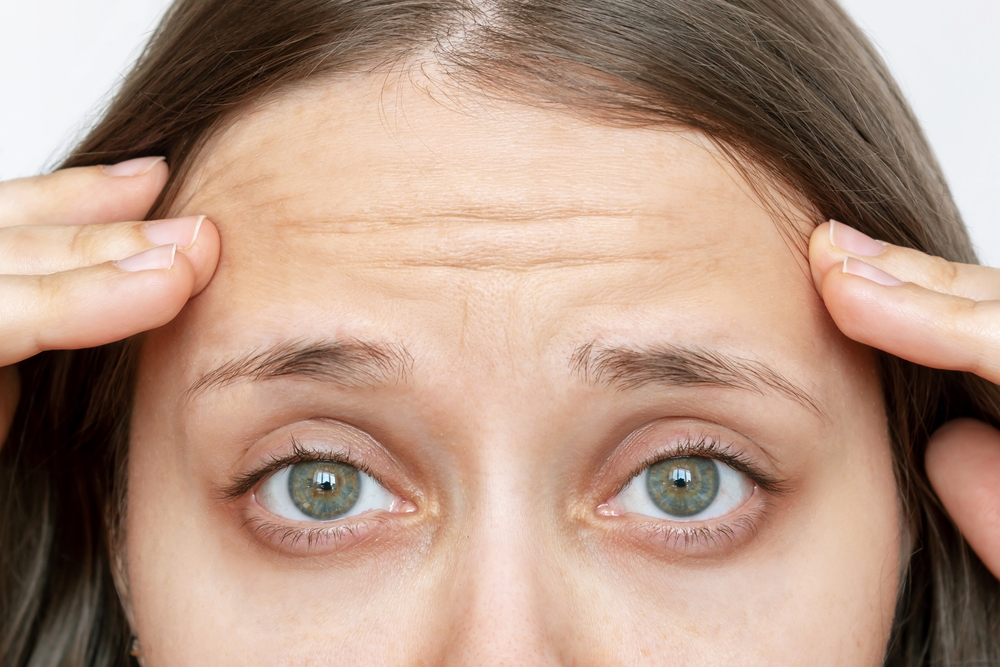

Forehead wrinkles are among the first visible signs of ageing and often appear earlier than expected. These lines result from repeated facial expressions, environmental exposure,
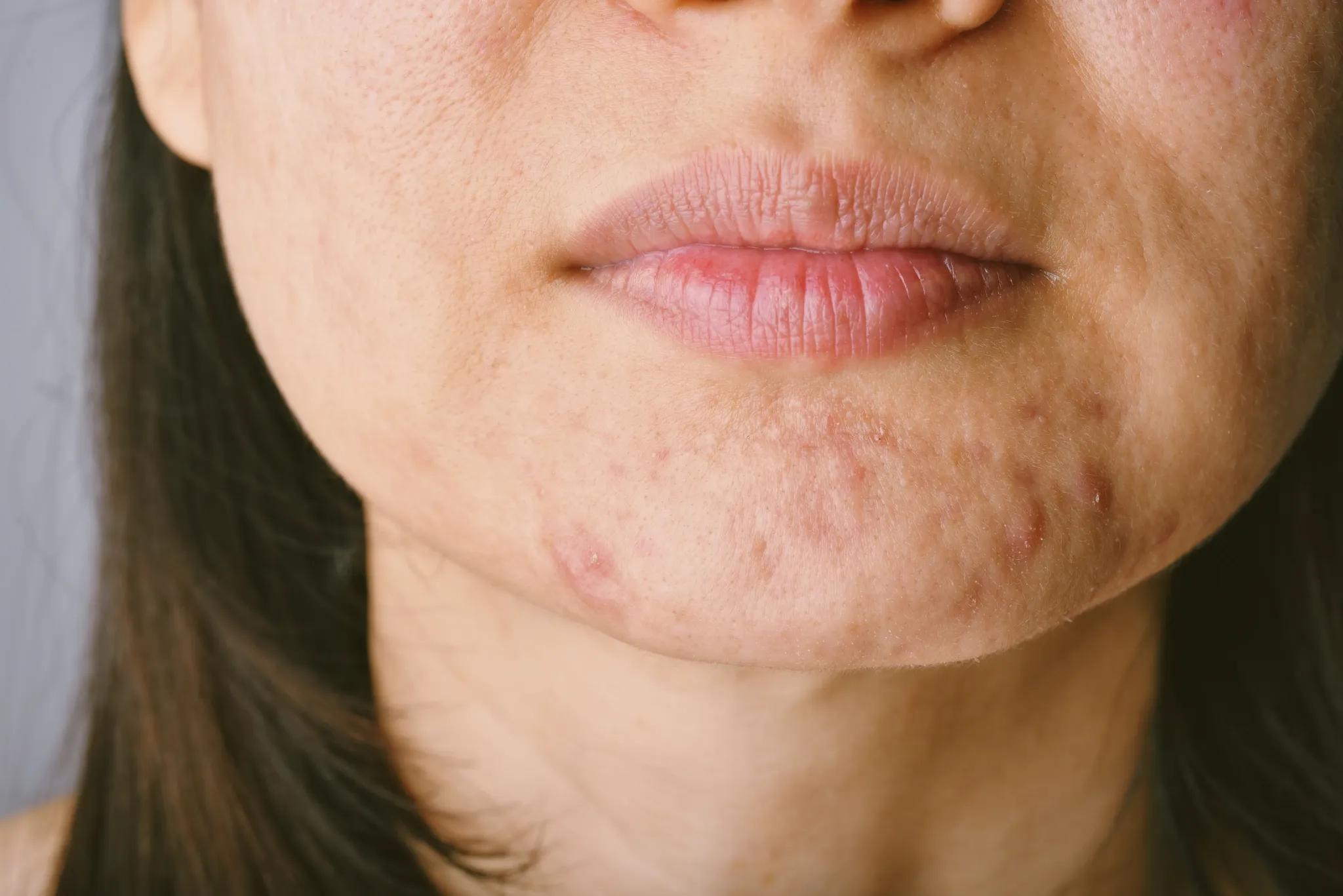
Struggling with chin breakouts that just won’t disappear? You’re not alone. Acne in this area tends to be stubborn and persistent, often showing up as
"*" indicates required fields
Excellent, we are always excited to meet a new face or to welcome back a familiar one. Contact us in the way that best works for you!
© 2022 Bondi Junction Cosmetic Clinic. All rights reserved.
Enter your details and we will contact you within 24 hrs.
"*" indicates required fields